Eprom (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) | Invention & Limitations
Published: 11 Jan 2026
EPROM is a type of memory chip that stores data permanently but can be erased and rewritten when needed. Once erased, new data can be programmed into it again.
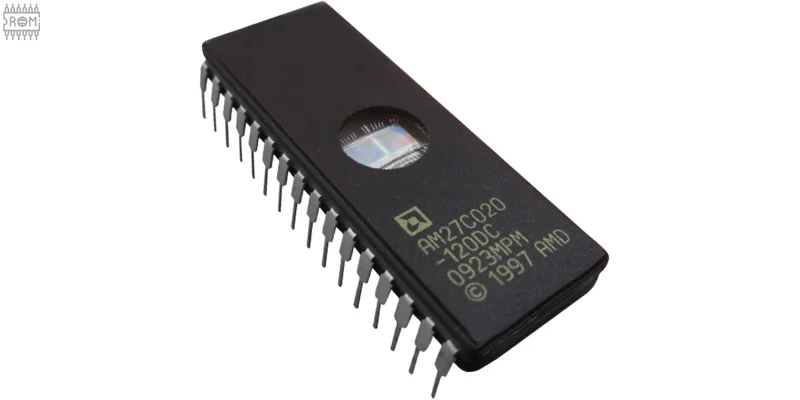

This made development faster, cheaper, and easier compared to a fixed ROM that couldn’t be changed. EPROM was commonly used in older computers, BIOS chips, and early electronic devices for storing firmware.
Who invented EPROM?
EPROM was invented by Dov Frohman, an Israeli engineer working at Intel, in 1971. He created it after discovering that stored data in a MOS transistor could survive even after power was removed.
What was the first EPROM chip?
The first EPROM ever made was the Intel 1702, released in 1971–1972.
- It had a small quartz window on top so UV light could erase the data.
- Its storage capacity was 2 kilobits (256 bytes), which was a big deal at that time.
Limitations of EPROM
- Needs UV light to erase (slow process)
- Can be erased only by removing the chip from the device
- Has a limited number of erase/write cycles
- Gets replaced by EEPROM and Flash later
EPROM vs EEPROM vs Flash
You can add a small comparison like:
- EPROM: Erased with UV light, requires physical removal.
- EEPROM: Stands for “Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory”, it can be reset electronically without removing it from device.
- Flash Memory: Faster, used in modern USBs and SSDs.
Data Retention
EPROM chips can store data for 10 to 20 years without losing information, as long as they are kept away from strong UV light. This made them reliable for long-term storage in older machines.
EPROM Programming Process
To write data to an EPROM:
- The chip is placed in a programmer device,
- A high voltage (typically around 12.5V) is applied to store the data,
- The programmer verifies every bit to ensure the data is stored correctly.
This process takes longer than today’s flash memory.
EPROM Erasing Process
- To erase the chip, you expose the window to ultraviolet light (253.7 nm) for about 15–30 minutes.
- After erasing, the entire chip becomes blank – EPROM cannot erase selected sections, only the full memory.
Variants of EPROM
There are two main versions:
- UV-EPROM: Has the quartz window (erasable).
- OTP-EPROM (One-Time Programmable): Same as EPROM, but no window, meaning it cannot be erased and can only be programmed once.
Why UV Light is Used
UV light destroys the charge trapped in the floating gate inside the transistor, which resets every bit to “1.” This is why the chip returns to its original blank state after erasing.
End of EPROM Era
EPROM remained popular until the early 2000s.
Eventually, it was replaced by:
- EEPROM (electrically erasable)
- Flash memory (faster, cheaper, easier to program)
Modern computers no longer use EPROM because newer technologies offer:
- Faster writing
- No UV light needed
- More erase cycles
- Better reliability
- Smaller physical size
Final Words
I hope it satisfies you. If you have any confusion, you can ask me in the comments. Thanks for your love Buddies.
EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) is a type of ROM; it is a chip that can be erased and rewritten without requiring the chip to be removed from the computer.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks