All Parts of a Computer | Explained with Images
Published: 7 Mar 2026
Are you getting confused? When you hear different names of computer parts and don’t know what each one actually does. No tension, here I will solve your problem. It’s easier than it looks:
Monitor
The monitor is the display/screen of your computer. It shows everything you do, whether you’re watching a video, editing a photo, or just typing, etc. It turns signals from your computer into a view you can see and control.

Modern monitors come in LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) and LED (Light-emitting Diodes) types, with features like sharp resolution, bright colours, and smooth refresh rates. The better the monitor, the clearer and more comfortable your experience feels while using your computer.
Keyboard
The keyboard is one of the main input devices for a computer. It lets you type letters, numbers, and commands so the computer can understand what you want it to do.

Note: Devices that allow you to give some type of instructions/commands or data to a computer are called input devices.
Keyboards come in too many different types: membrane keyboards, which are soft and quiet, and mechanical keyboards, which are clicky and more durable. Some keyboards are wired, while others connect wirelessly via Bluetooth.
Beyond typing, keyboards also have special keys for shortcuts, controlling volume, and other functions that make using a computer faster and easier.
Mouse
The mouse is another input device for your computer. It helps you control the movement of the cursor on the screen, click on things, and interact with programs easily.

There are two main types: optical mice, which use a light sensor to detect movement, and laser mice, which are more precise and work on almost any surface. Mice can be wired or wireless, giving you flexibility in how you use them. Some also have extra buttons for shortcuts, scrolling, or gaming, making navigation faster and smoother.
Computer Case

A computer case is the outer box that holds and protects all the main parts of a computer, like the motherboard, CPU, RAM, power supply, and storage drives. It keeps everything organized, safe from dust, and helps manage airflow so the system stays cool while running.
CPU
The CPU stands for central processing unit, is a chip. It’s a small, flat piece of silicon packed with millions of tiny circuits. These circuits handle all the calculations and instructions that make your computer run by telling the other parts what to do. It is basically the brain of your computer.
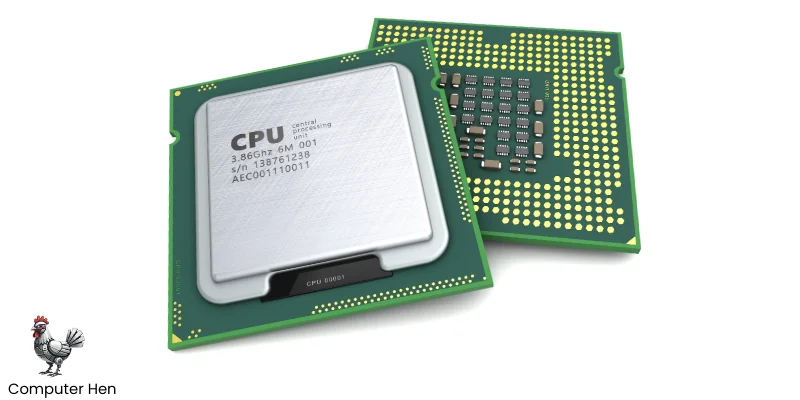

Even though it’s tiny, it’s super powerful and sits on the motherboard, usually under a heatsink or fan to keep it cool. Think of it like a tiny brain controlling the whole system.
Modern CPUs have multiple cores, which let them do many tasks at the same time, making your computer faster. Its speed is measured in gigahertz (GHz), which tells you how many instructions it can process per second. A strong CPU makes everything from browsing to gaming run smoothly.
GPU
The GPU stands for graphics processing unit, is the part of your computer that handles everything you see on the screen.

It creates images, videos, and animations and sends them to the monitor. There are two types of GPU:
- Integrated GPU – Built into the CPU or motherboard. Good for basic tasks like browsing or watching videos.
- Dedicated GPU – A separate card with its own memory, much stronger for gaming, video editing, 3D design, and AI tasks.
A good graphics card makes games smoother, videos sharper, and creative work faster. Basically, it’s the artist and visual engine of your computer.
Motherboard
The motherboard is like the main hub of your computer. It’s a big circuit board that connects all the parts-CPU, RAM, storage drives, GPU, and more so they can communicate with each other.
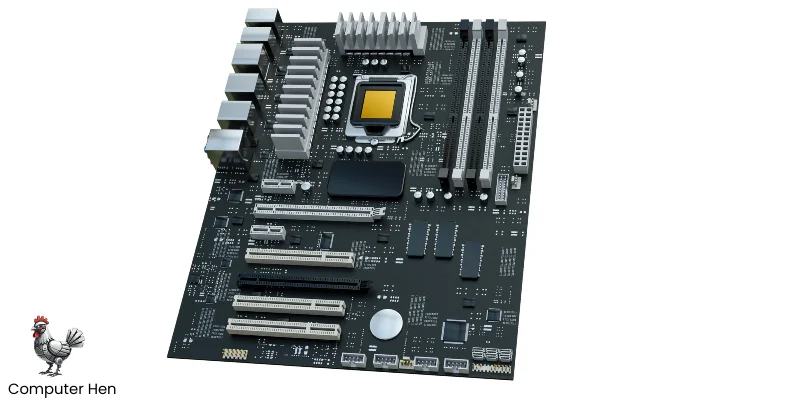

It also has slots and ports for connecting external devices like your keyboard, mouse, and monitor. A good motherboard ensures everything works smoothly together, and it can even affect how fast or upgradeable your system is. Basically, without the motherboard, the computer parts can’t talk to each other.
RAM
RAM stands for Random Access Memory, and it’s one of the most important parts of your computer. Think of it as short-term memory for your system. It temporarily stores the data and programs your computer is using right now so the CPU can access them quickly.
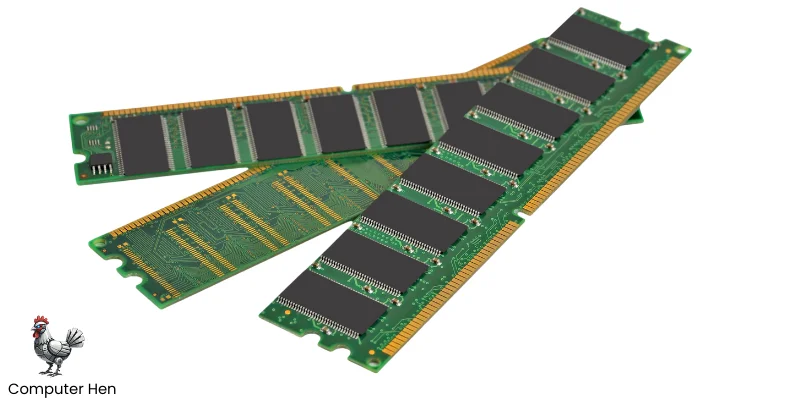
The more RAM you have, the more programs you can run smoothly at the same time. Unlike storage drives, RAM loses its data when the computer is turned off, which is why it’s only for temporary tasks and is called volatile memory. Having enough RAM makes your computer feel quick and responsive.
ROM
ROM stands for Read-Only Memory. It’s a type of computer memory that stores important instructions your computer needs to start up, like the BIOS or firmware.
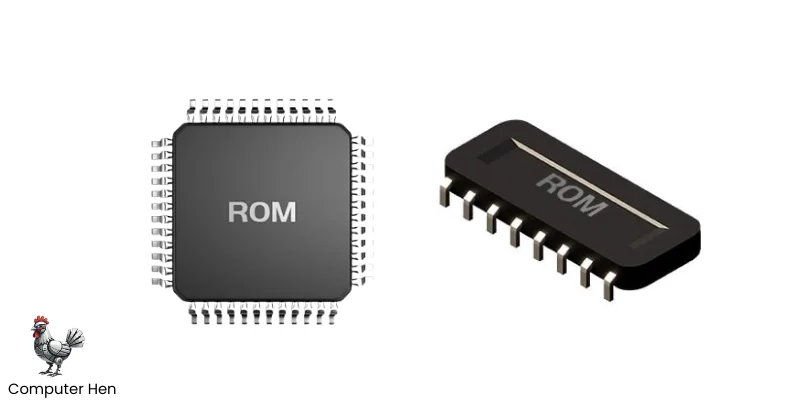
Unlike RAM, the data in ROM doesn’t disappear when you turn off the computer, which is why it’s called non-volatile. You can read the information stored in ROM, but you usually cannot change it, or it’s very hard to modify. It’s like the permanent guidebook your computer uses to get ready every time you switch it on.
Storage
These are all types of storage drives where your computer keeps data, files, and programs. Let me break it down simply:
1. HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
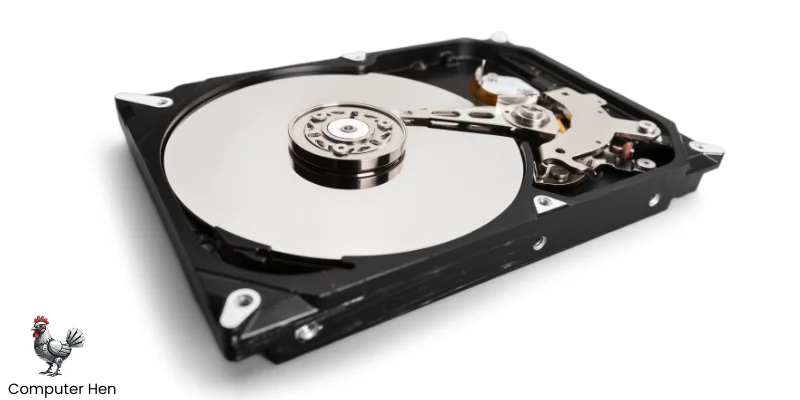

- Uses spinning magnetic disks to store data.
- Slower than modern drives, but usually cheaper and comes in large sizes.
- Good for storing lots of files, videos, or backups.
2. SSD (Solid State Drive)
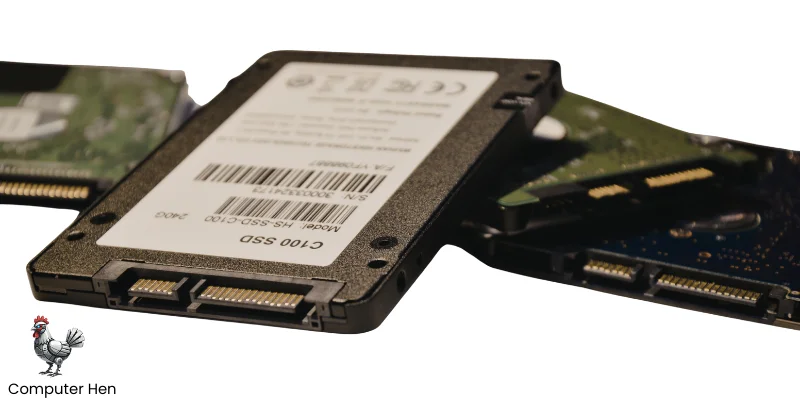

- Uses flash memory, no moving parts.
- Much faster than HDDs, so programs and files open quickly.
- More expensive per GB, but it makes your computer feel snappy.
3. NVMe SSD

- Extremely fast read and write speeds, ideal for gaming, video editing, and heavy software.
- An advanced type of SSD that connects directly to the motherboard through a special slot.
Disk Drive
A disk drive is a device in your computer that reads and writes data on storage disks. These disks can be CDs, DVDs, or Blu-ray discs.
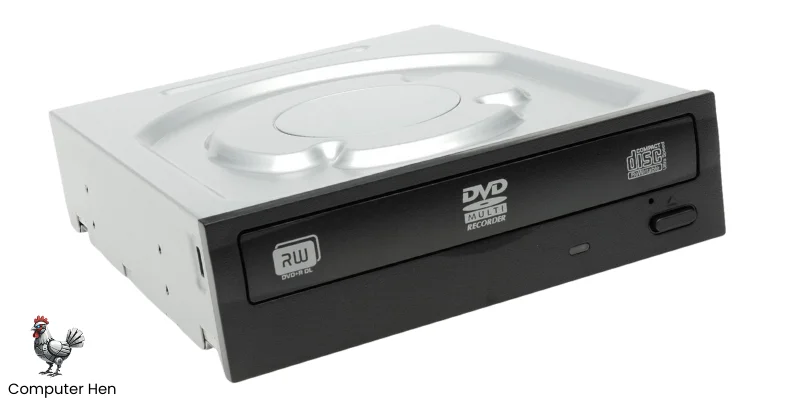

Disk drives can be internal (inside your computer) or external (connected via USB). They use a laser to read the data stored on the disk and sometimes to write new data. While they are less common now because of SSDs and cloud storage, disk drives are still used for installing software, watching movies, or backing up files.
Slots
A slot is basically a place on the motherboard where you can plug in a component. Think of it like a socket or a connector.
- RAM Slots (Memory Slots): Hold the RAM sticks for temporary memory.
- PCIe Slots (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express): For graphics cards, sound cards, network cards, and other expansion cards.
- M.2 Slots: For ultra-fast SSDs (NVMe or SATA).
- SATA Ports/Slots: Connect HDDs, SSDs, and optical drives for storage.
- CPU Socket: Where the CPU chip sits on the motherboard.
- Power Connector Slots: Connect the power supply to the motherboard and components.
- Fan/CPU Cooler Slots: For connecting cooling fans or liquid cooling pumps.
- Front Panel Header Slots: Connect buttons, LEDs, and ports on the computer case to the motherboard.
Ports
A port is a connector on your computer that lets you attach external devices. It’s like a doorway for data or power to flow in and out of your computer.
- USB Ports: For connecting keyboards, mice, flash drives, printers, and other devices. Comes in types like USB-A, USB-C, and USB 3.0/3.1 for faster data transfer.
- HDMI Port: Connects your computer to a monitor, TV, or projector to show video and audio.
- DisplayPort: Another video port for monitors, often used for high resolution or high refresh rates.
- Ethernet Port (RJ45): Connects your computer to wired internet networks.
- Audio Ports: Usually 3.5mm jacks for headphones, speakers, and microphones. It has separate ports for mic in, line out, and headphones.
- Power Connector Port: Where the power supply cable connects to give electricity to the PC.
- VGA/DVI Ports: Older video ports, still on some computers, for monitors that don’t support HDMI.
Fan
Buddy, the computer fan is a simple but very important part. Its main job is to keep your computer cool by moving air through the case and over hot parts like the CPU, GPU, and power supply.
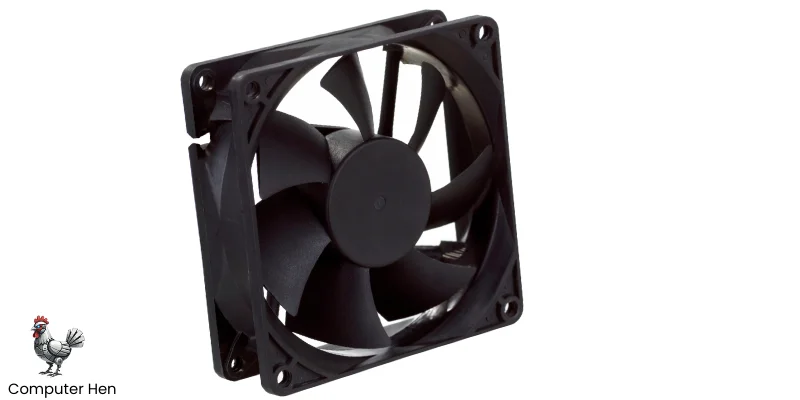

Without fans, your components could overheat, slow down, or even get damaged. Fans come in different sizes and types:
- Case Fans: Move air in and out of the computer case.
- CPU Fans: Sit on top of the processor to cool it directly.
- GPU Fans: Built into graphics cards to cool the GPU.
Power Supply
The Power Supply Unit (PSU) is the part that gives electricity to your whole computer. Without it, nothing would work.
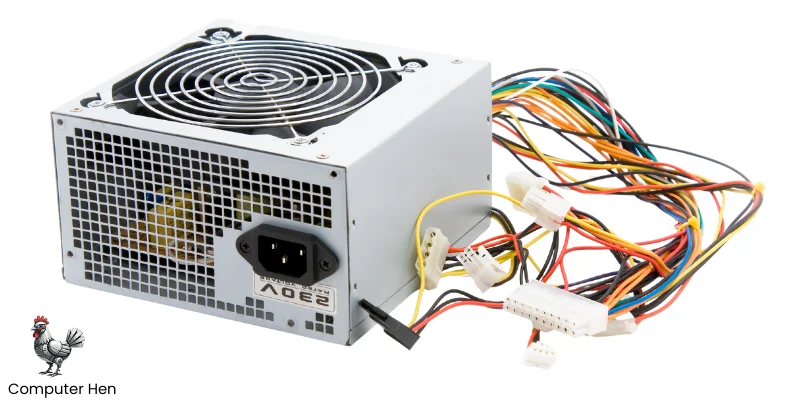

It takes the electricity from your wall outlet and converts it into the right voltage and current for the cpu, GPU, motherboard, drives, and other components. PSUs come in different wattages, which tells you how much power they can provide.
A good PSU keeps your system stable, safe, and running smoothly, because low and high power can easily ruin a computer.
Final Words
Now you’ve seen how every part of a computer has its own job, from the screen that shows your work to the tiny chip that thinks for the whole system.
Once you understand what these parts do, the whole machine starts to make sense. You don’t feel confused anymore because each component has a clear purpose.
With this knowledge, you can choose the right parts, solve basic problems, and understand your computer with confidence.
FAQ’s
Sound card is a part of your computer that handles all the audio. It turns digital signals from your computer into sounds you can hear through speakers or headphones.
Some sound cards are built into the motherboard (integrated), while others are separate (dedicated) for better quality. They make music, videos, games, and recordings sound clear and smooth.
Modem connects your computer to the internet through your Internet Service Provider (ISP). It translates the internet signal from your provider into a signal your computer can use.
Router, on the other hand, shares that internet connection with multiple devices in your home or office, either through Wi-Fi or cables.
In short:
- Modem = brings internet in,
- Router = shares internet to all devices.
Optical sensors detect light, movement, or position. In laptops, they can be part of the touchpad (detecting finger movement), the camera (capturing images), or even ambient light sensors (adjusting screen brightness automatically).
They help devices “see” or respond to your actions without you touching buttons.
High-end PCs get very hot because powerful CPUs and GPUs make a lot of heat.
- Heat pipes are sealed pipes with liquid inside that quickly carry heat away from the CPU or GPU to a big metal radiator, where fans blow the heat out.
- Liquid cooling systems work similarly but on a bigger scale. Coolant flows through tubes, absorbs heat from hot parts, moves it to a radiator, and then fans push the heat away.
Basically, both systems take heat away fast so the computer stays cool and runs faster without overheating.
RAID controller manages multiple hard drives or SSDs together to act as one big, smarter drive.
- It can speed up performance (RAID 0), backup data automatically (RAID 1), or do both (other RAID types).
- You find RAID controllers in servers, gaming PCs, or workstations where speed or safety of data is important.
BIOS chip is a tiny chip on your motherboard with special instructions.
- When you turn on your computer, the BIOS wakes up the CPU, memory, and storage, checks that everything is working, and then loads the operating system.
- Think of it like a morning checklist: it makes sure your computer is ready to work before you start using it.
Expansion cards are extra cards you can plug into your motherboard to give your computer new abilities.
- Sound cards improve audio quality for music, games, or recordings.
- Capture cards let you record video from cameras, consoles, or other devices.
- There are also network cards, TV tuner cards, or Wi-Fi cards.
Basically, if your computer can’t do something by default, an expansion card can add that feature.
CMOS battery is a tiny battery on the motherboard.
- It powers the CMOS chip, which stores basic system settings like time, date, and hardware configurations, even when your PC is turned off.
- Without it, your computer would forget the clock and some settings every time you shut it down.
- Network cables (like Ethernet) carry data as electrical signals between your computer and a network or internet. They’re fast and reliable.
- Wireless adapters (Wi-Fi cards or USB dongles) let your computer send and receive data through radio waves, connecting to Wi-Fi networks without cables.
Both basically act as a bridge to get your computer online and communicate with other devices.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks